Hair loss can affect confidence and appearance, especially in men experiencing male pattern baldness. Among the treatments available, Finasteride has emerged as one of the most reliable options for slowing hair thinning and supporting regrowth.
Unlike topical solutions, Finasteride works from within the body, targeting the hormonal processes that cause hair follicles to shrink over time. With consistent use and proper guidance, it can help many men maintain their hair and regain a fuller, healthier-looking scalp.

Table of Contents
What Is Finasteride for Hair Loss?
Finasteride is a prescription medication primarily used to treat male pattern baldness (androgenetic alopecia) and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) — an enlarged prostate (Mayo Clinic overview).
Originally developed for prostate health, Finasteride for hair loss was later found to block the hormone DHT (dihydrotestosterone), which is responsible for shrinking hair follicles.
By reducing DHT levels, Finasteride helps slow hair thinning and support regrowth in men experiencing male pattern hair loss.
Finasteride Tablet Names and Dosage Options
Finasteride is available under two main brand names:
- Propecia® (1 mg): Used for treating hair loss in men.
- Proscar® (5 mg): Prescribed for prostate enlargement (BPH).
For hair loss, doctors typically recommend Finasteride 1 mg daily, which is the standard and clinically proven dosage for improving hair density and preventing further shedding.
Quick fact: The 1 mg Finasteride tablet blocks about 60–70% of DHT, which is enough to stop most genetic hair loss in men.
In this article, we’ll focus mainly on Finasteride for hair loss, exploring how it works, how effective it is, and what results you can expect from consistent use.
Why Finasteride Is Used for Hair Loss
Doctors discovered that men taking Finasteride for prostate issues also noticed significant hair regrowth.That finding led to its approval as an effective hair loss treatment for men — now one of the most widely prescribed worldwide.
How to Get a Finasteride Prescription Safely
If you’re wondering how to get finasteride for hair loss, the first step is consulting a licensed dermatologist or doctor. Finasteride is a prescription medication, so it cannot be bought over-the-counter. Once prescribed, you can obtain it from a local pharmacy or a verified online pharmacy. Always ensure you are using genuine finasteride hair loss tablets for safe and effective results.
How Finasteride Works
Understanding how Finasteride works:
explain why it’s so effective at stopping thinning and promoting regrowth.
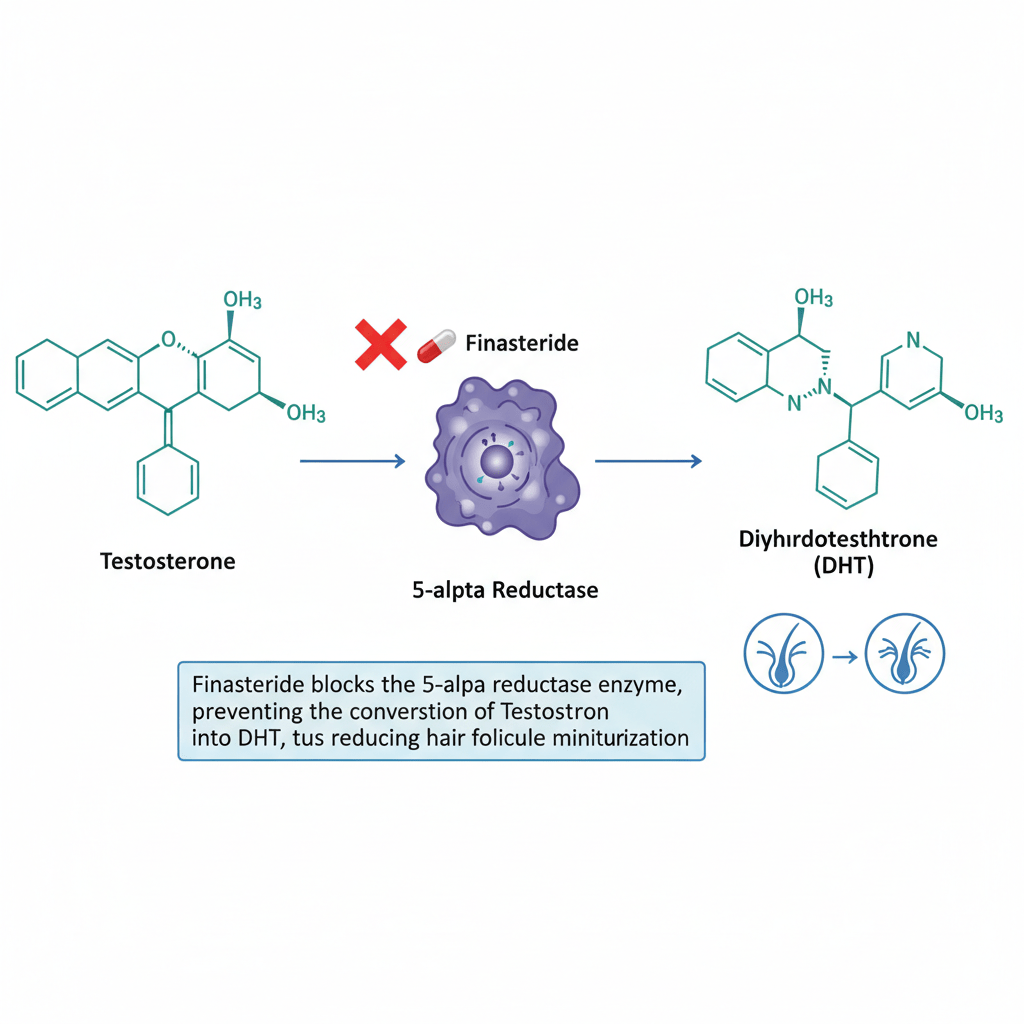
The Role of DHT (Dihydrotestosterone)
DHT is a powerful hormone derived from testosterone. While it’s essential for normal male development, in some men it can become overactive in the scalp, causing hair follicles to shrink — a process known as miniaturization.
Over time, this miniaturization leads to thinner, weaker hair strands and eventually visible baldness.
Finasteride’s Action On The Enzyme
Finasteride works by blocking an enzyme called 5-alpha reductase, which converts testosterone into DHT.
By lowering DHT levels, Finasteride helps:
- Slow down or stop hair loss
- Allow miniaturized follicles to recover
- Support thicker and healthier regrowth
Clinical research shows that Finasteride can reduce DHT in the blood by up to 70% and in the scalp by more than 90%, effectively protecting hair follicles from further damage
Why It’s Effective for Male Pattern Baldness
By targeting the root cause of hair loss, Finasteride helps preserve existing hair and stimulate new growth over time.
It not only reduces shedding but also extends the hair’s natural growth phase — leading to thicker, fuller coverage and stronger strands.
How Long Does Finasteride Take to Work? (Before & After Results)
When taken daily at the 1 mg dose, Finasteride for hair loss has been clinically proven to reduce shedding and promote regrowth in men with androgenetic alopecia. Because hair growth cycles progress slowly, most users begin noticing visible improvements after 3 to 6 months of consistent use.
During the first few months, some men may notice a slight increase in shedding — this is completely normal and temporary. It usually means older hairs are falling out to make way for stronger new growth.
By around 3 to 6 months, shedding typically slows down, and hair texture begins to feel thicker and healthier. Visible thickening and fuller coverage often become noticeable between 9 to 12 months of continuous use.
Consistency is essential. If Finasteride is stopped, DHT levels can rise again, and hair loss may gradually return within several months.
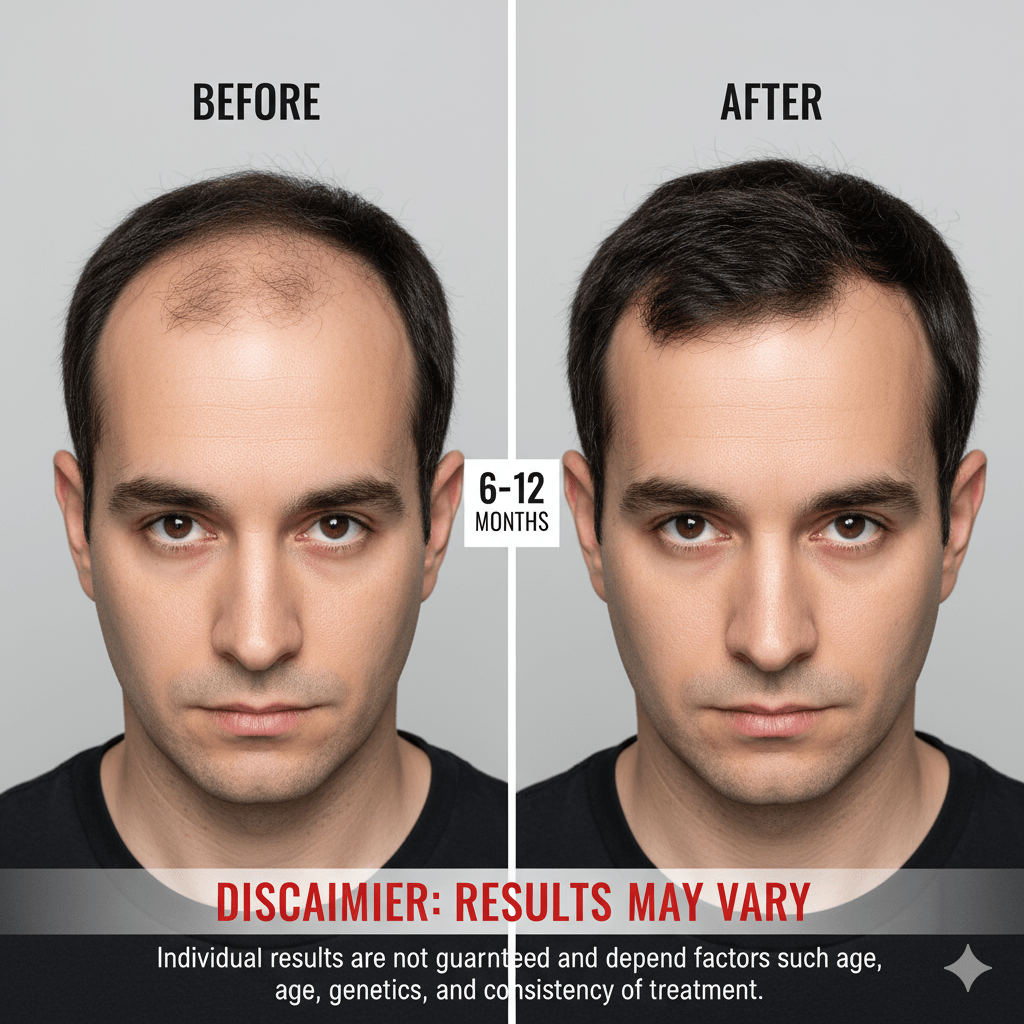

Finasteride Results Timeline
- After 3–6 months: Early signs of reduced shedding and stronger hair strands start to appear.
- After 9–12 months: Visible regrowth and fuller coverage become noticeable, especially around the crown and hairline.
- After 1 year: Around 90% of men report visible improvement, with an average 14% increase in hair count.
- After 2 years: Hair density improves by about 16%, and results become more stable.
- After 5–10 years: Nearly all users (about 99%) maintain their results or experience further improvement, with long-term prevention of future hair loss.
Finasteride’s biggest strength lies not only in helping regrow hair but also in stopping ongoing thinning and maintaining scalp health over time.
Key takeaway: Finasteride works gradually but provides lasting results:
- 3–6 months: Early improvement
- 9–12 months: Visible regrowth
- 2+ years: Stable, maintained results
Oral vs. Topical Finasteride: Which Works Better?
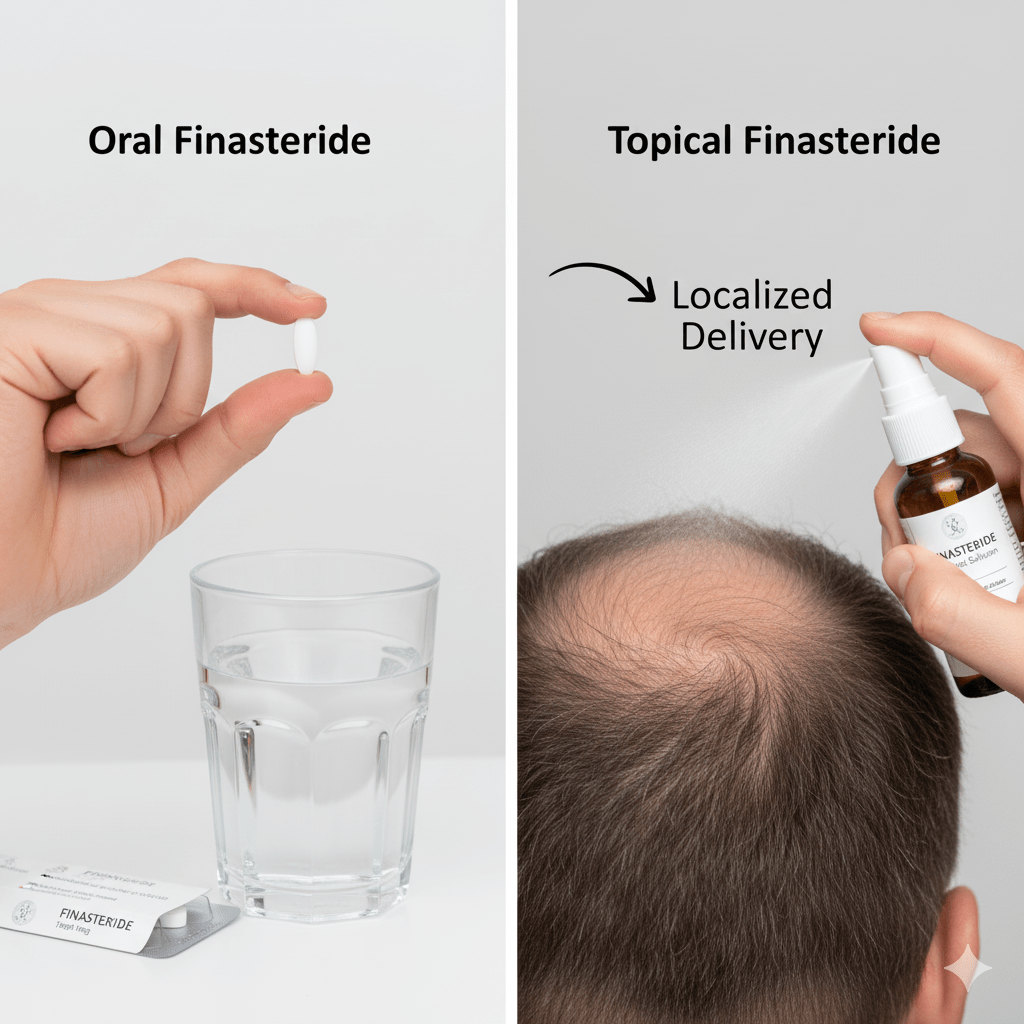
Topical Finasteride for hair loss
What It Is:
Topical Finasteride is a solution or spray applied directly to the scalp. Unlike oral tablets, it targets hair follicles locally rather than affecting the whole body.
How It Works:
- Blocks DHT (dihydrotestosterone) specifically in the scalp.
- Reduces follicle miniaturization and helps maintain existing hair.
- Can be combined with Minoxidil for enhanced regrowth results.
Key Points:
- Direct application means less absorption into the bloodstream, focusing on the areas that need it most.
- Can be used by men who want to avoid systemic DHT reduction initially.
- Often recommended as a first step before starting oral Finasteride for those concerned about side effects.
Tip:
Topical Finasteride is most effective with consistent, daily use. Hair growth improvements are usually noticeable after several months, similar to oral treatment but in a more targeted way.
Note: Topical Finasteride is not yet FDA-approved, but early research and real-world use show promising results for reducing scalp DHT with fewer systemic effects. It’s often prescribed off-label by dermatologists.
Oral Finasteride for Hair Loss
What It Is:
Oral Finasteride is an FDA-approved tablet, usually taken at a 1 mg daily dose for hair loss. It works systemically, meaning it affects the entire body rather than just the scalp.
How It Works:
- Blocks the conversion of testosterone to DHT throughout the bloodstream.
- Reduces DHT levels in the scalp, slowing hair follicle miniaturization.
- Supports long-term maintenance of existing hair and promotes regrowth in men with androgenetic alopecia.
Key Points:
- Systemic action reduces DHT levels both in the scalp and in the blood.
- Clinically proven to maintain or improve hair coverage in most men.
- Often prescribed when topical treatment alone is insufficient or for faster overall results.
Tip:
Hair growth results appear gradually, typically within 3–6 months, with full effects visible around 9–12 months. Regular, consistent use is essential for maintaining benefits.
Which Finasteride Is Best?(Topical & Oral)
Choosing between oral and topical Finasteride depends on your comfort, health goals, and how your body responds to treatment.
- Topical Finasteride is ideal if you want to target hair loss locally and minimize systemic side effects. It blocks DHT directly in the scalp and is often chosen as a safer starting option for men concerned about hormonal effects.
- Oral Finasteride (1 mg) remains the most effective and clinically proven treatment for male pattern baldness. It reduces DHT throughout the body and offers long-term results in maintaining and regrowing hair.
Best approach:
If you’re new to treatment, many dermatologists recommend starting with topical Finasteride or a low dose of oral Finasteride, then adjusting based on your results and tolerance.
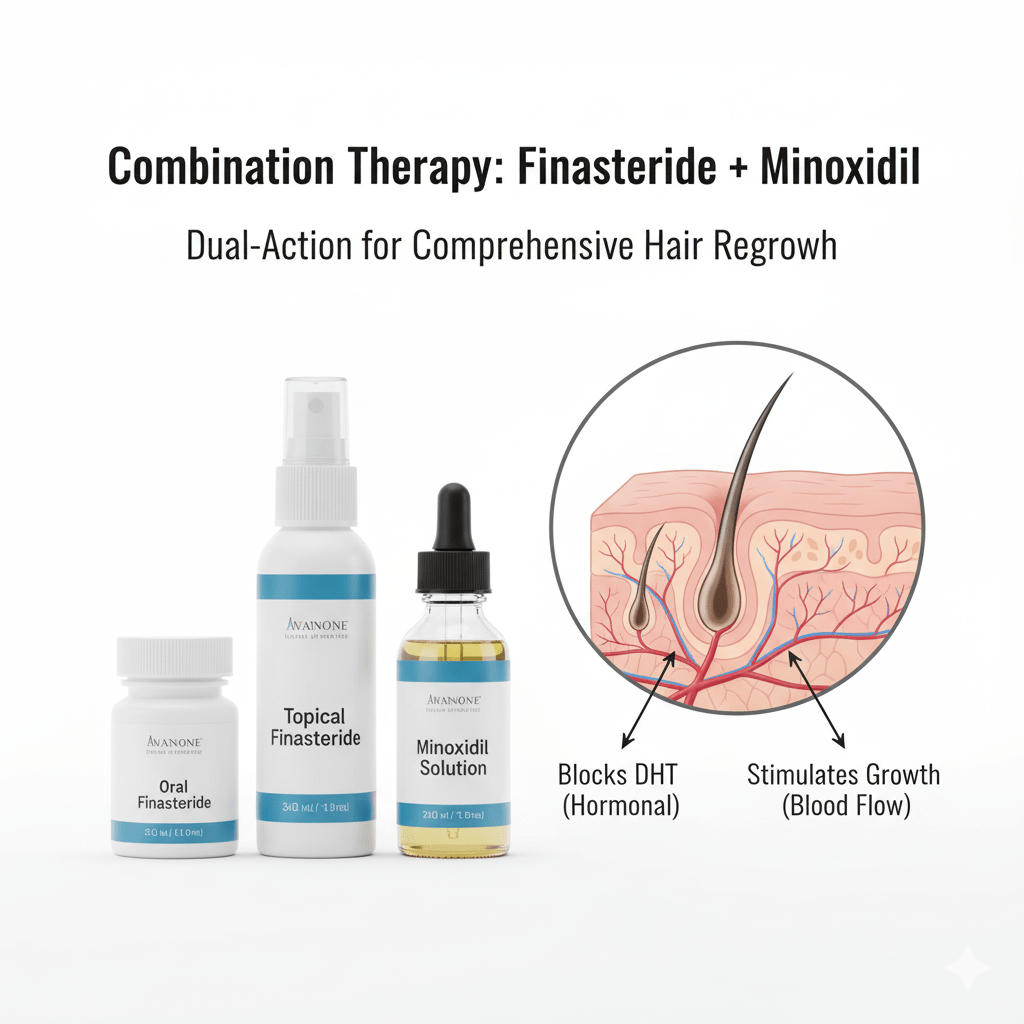
Combination Therapy — Finasteride + Minoxidil for Better Results
Using Finasteride and Minoxidil together can target hair loss from two different angles
- Finasteride reduces DHT levels (the hormone responsible for follicle shrinkage).
- Minoxidil boosts scalp blood flow, improving oxygen and nutrient delivery to hair roots.
Clinical studies show that this dual-action approach helps achieve stronger regrowth and reduces shedding more effectively than either treatment alone.
Tip: Start one medication at a time (usually Minoxidil first) before combining, and always follow your dermatologist’s guidance.
Topical Finasteride is also being studied for female pattern hair loss, especially in combination with Minoxidil, to maintain results achieved from oral treatment.(study of topical finasteride spray solution).”
Finasteride Side Effects
Before starting Finasteride for hair loss, it’s important to understand potential side effects. Most are mild, short-term, and reversible, but some require monitoring.
Short-Term Side Effects
Some users may notice effects after 1 month or 3 months of taking Finasteride. These include:
- Temporary hair shedding (common during the first months)
- Headaches
- Mild fatigue
- Gastrointestinal discomfort
Sexual Side Effects
Sexual side effects are often a concern. These may appear in the first months of treatment:
- Reduced libido
- Erectile difficulties
- Decreased semen volume
These effects are usually temporary and resolve either with ongoing use or after stopping Finasteride.
Long-term studies show an overall adverse reaction rate of less than 1% — most men tolerate Finasteride well.
Long-Term & Rare Side Effects
Though uncommon, some men may experience long-term effects such as:
- Gynecomastia (breast enlargement)
- Weight changes
- Persistent fatigue or mood changes
These long-term side effects are rare and mostly reversible after discontinuation.
Safety tip:
- Tablets are coated for safety — do not crush or break them.
- Men should avoid donating blood during treatment and for 6 months after stopping.
Post-Finasteride Syndrome (PFS)
While extremely rare, some men report persistent symptoms after stopping Finasteride, known as Post-Finasteride Syndrome (PFS).
- Symptoms may include low libido, fatigue, depression, or emotional blunting.
- PFS can occur with both 1 mg (Propecia®) for hair loss and 5 mg (Proscar®) for prostate treatment.
For a detailed guide on Post-Finasteride Syndrome, see our full PFS post.
Recovery & Reversibility
Most side effects from Finasteride:
- Go away with continued use or after stopping the medication
- Are not permanent for the majority of users
- Can be minimized by following your doctor’s dosage recommendations
Finasteride Alternatives for Hair Loss
Not everyone responds the same to Finasteride. Some prefer alternatives like:
- Minoxidil (topical/oral)
- DHT-blocking shampoos (Saw Palmetto, Ketoconazole, Caffeine)
- PRP therapy
- Hair transplants
- Microneedling
FAQs about Finasteride
How long does Finasteride take to work?
Most men start noticing reduced hair shedding within 3 to 6 months of daily use. Visible thickening or regrowth usually appears after about 12 months of consistent treatment.
Can I stop taking Finasteride once my hair grows back?
If you stop taking Finasteride, DHT levels will rise again, and hair loss may resume within a few months. Continued use is recommended to maintain long-term results.
Can I use Finasteride and Minoxidil together?
Yes. Many dermatologists recommend combining Finasteride (to block DHT) with Minoxidil (to stimulate growth). Together, they address both the hormonal and growth-cycle causes of hair loss.
Does Finasteride work for everyone?
Finasteride is most effective for men with mild to moderate hair loss. Results can vary depending on age, genetics, and the duration of baldness before starting treatment.
Are Finasteride results permanent?
Results last only while the medication is taken. Once discontinued, DHT activity can cause gradual hair thinning to return.
Conclusion
Finasteride remains one of the most trusted treatments for male pattern hair loss. By blocking DHT, it helps most men slow hair thinning, preserve existing strands, and even regain lost hair over time.
For optimal results, Finasteride can be combined with topical solutions like Minoxidil, which many men use to enhance regrowth.
With consistent use and professional guidance, Finasteride offers long-term, evidence-based results — helping men regain both hair and confidence.
Related Posts
Understand the causes of hair loss and explore the most effective treatment options.
See how Minoxidil can complement Finasteride for better hair regrowth results.
Learn about potential side effects and recovery tips for Finasteride users.
Check the stages of male pattern baldness to understand severity and progression.