Introduction
Want to know how to prevent pimples from appearing on your face? Discover 7 proven, dermatologist-backed tips along with product recommendations for clearer, healthier skin.
But here’s the good news: most breakouts are preventable. In this guide, you’ll learn 7 proven, dermatologist-recommended strategies to keep acne from appearing on your face. These tips are simple, practical, and perfect for anyone dealing with occasional or frequent breakouts.
Table of Contents
Signs & Symptoms of Pimples on the Face
Not all pimples are the same. Some begin as small bumps, such as blackheads or whiteheads — these are called non-inflammatory because they are not red or painful.
When a clogged pore traps bacteria, such as Cutibacterium acnes, the area can become irritated and swollen. This is when pimples turn inflammatory, appearing as red, painful spots like papules or pustules. Even mild acne can develop into more severe breakouts if not treated promptly.
1. Mild Acne: Non-Inflammatory Pimples
Mild Pimples (Non-Inflammatory Acne)”Mild pimples are the early stage of acne. They are not red, swollen, or painful and form when pores become clogged with oil, bacteria, and dead skin cells, but without causing inflammation.
Mild/Non-inflammatory Types:
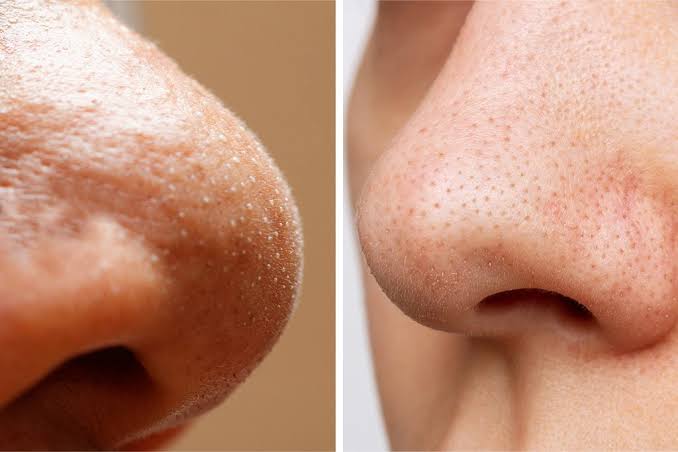
- Whiteheads (Closed Comedones): Small, white or skin-colored bumps that remain under the skin’s surface.
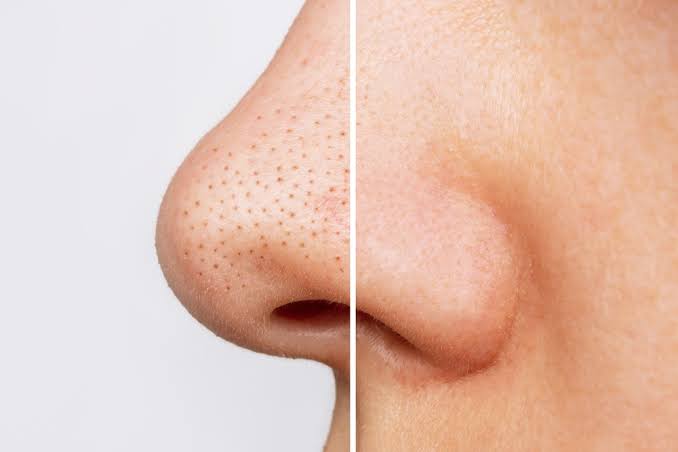
- Blackheads (Open Comedones): Tiny black dots that form in open pores when trapped oil oxidizes.
2. Moderate to Severe Acne: Inflammatory Pimples
Inflammatory pimples are red, swollen, and often painful. They occur when clogged pores become infected with bacteria, triggering the body’s immune response and causing inflammation.
Common Inflammatory Types:
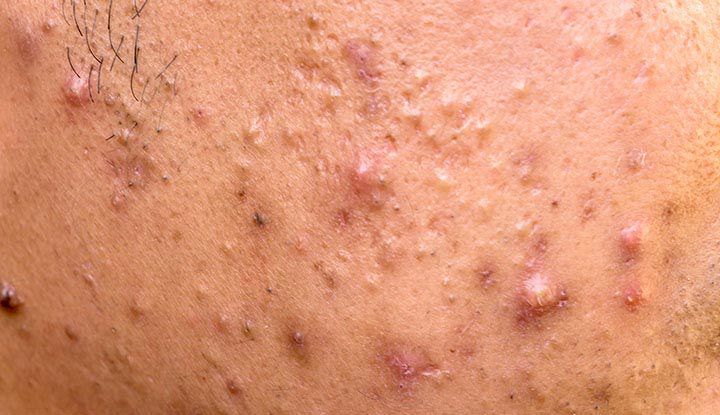
- Papules: Small, red bumps without pus — tender to the touch.
- Pustules: Classic pus-filled pimples — red base with a white or yellow head.
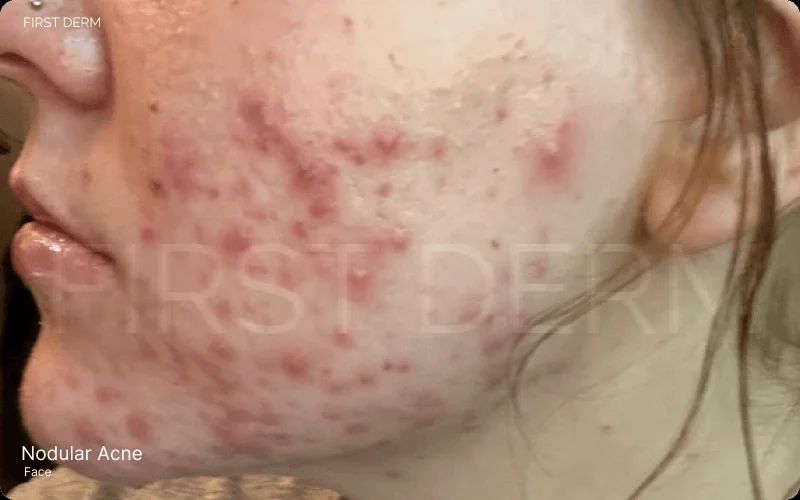
- Nodules: Large, firm, deep bumps — very painful and long-lasting.
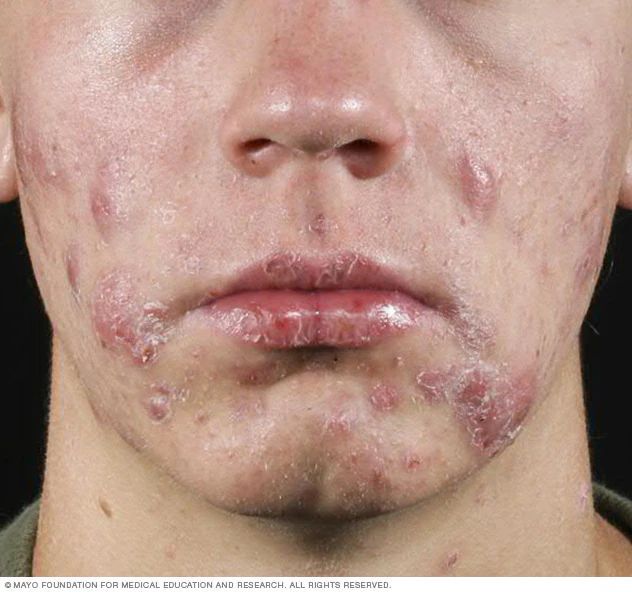
- Cysts: Soft, pus-filled lumps deep under the skin — may leave scars.
Why Pimples Appear: Causes Explained
Pimples don’t appear randomly — there’s a clear cycle happening beneath your skin. Several factors contribute to breakouts, including excess oil production, clogged pores, bacterial growth, and hormonal imbalances such as PCOS. Understanding this cycle is key to preventing pimples effectively.
- Excess Oil Production (Sebum): Your skin naturally produces oil to stay moisturized. However, during puberty, hormonal changes, or periods of stress, the sebaceous glands can become overactive and produce excess sebum.
- Mixing with Dead Skin Cells: Excess oil combines with dead skin cells on the surface. Instead of shedding naturally, this mixture becomes sticky and clogs the pores.
- Clogged Pores (Follicles): The blocked pore traps oil and dead skin cells inside, creating an ideal environment for bacteria to grow.
- Bacterial Growth: Cutibacterium acnes, a type of bacteria naturally present on the skin, begins multiplying inside the clogged pore, which triggers your immune system.
- Inflammation and Swelling: Your immune system sends white blood cells to fight the bacteria, resulting in redness, swelling, and pain — this is when a pimple becomes visible.
- Pimple Formation: The outcome is a visible spot — which may be a whitehead, blackhead, papule, pustule, or a deeper nodule or cyst, depending on the severity.
According to the NHS, pimples form when excess oil and dead skin cells block your pores. Bacteria can grow inside these blocked pores, leading to swelling, redness, and the formation of visible spots.
7 Effective Ways to Prevent Breakouts on the Face Naturally

1. Use a Salicylic Acid Face Wash Daily
Salicylic acid penetrates deep into the pores to remove oil and dead skin. It’s especially effective for small acne on the face.
- Neutrogena Oil-Free Acne Wash
- CeraVe Renewing SA Cleanser
- Clean & Clear Foaming Face Wash
Use twice daily — morning and night — for best results.
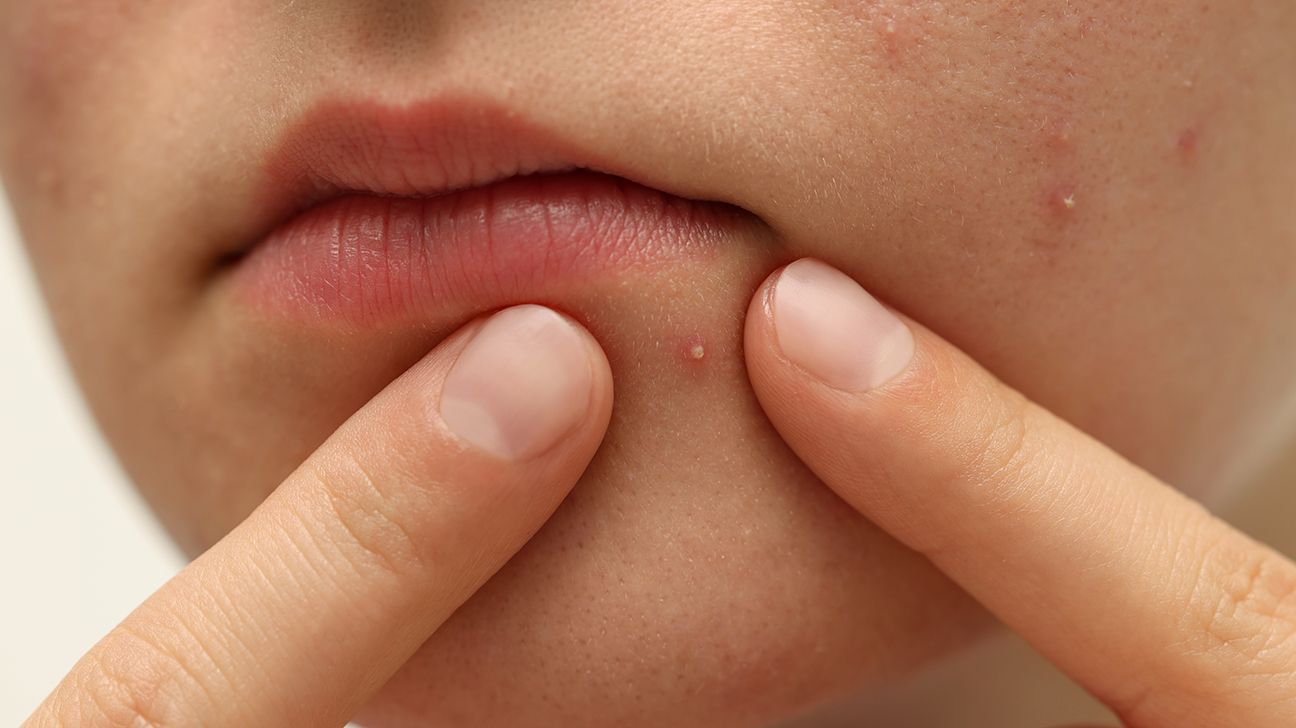
2. Avoid Touching or Popping Pimples
Touching your face spreads bacteria and oil, worsening acne. Popping pimples can lead to scarring and deeper infections.
3. Clean Your Pillowcase and Phone Screen Regularly
Change your pillowcase 2–3 times a week. Clean your phone screen daily with alcohol wipes to prevent bacteria transfer.
4. Don’t Overwash or Scrub Your Skin
Overwashing or scrubbing your skin can irritate it and cause more breakouts. Stick to gentle cleansing twice daily.
5. Eat Clean: Limit Sugar, Dairy, and Greasy Foods
Certain foods can trigger breakouts. Limit sugar, dairy, and greasy foods. Instead, focus on:
- Leafy greens
- Nuts & seeds
- Omega-3-rich foods (like flaxseed or fish)
6. Manage Stress
Stress releases cortisol, which increases oil production and can trigger breakouts. Try deep breathing, journaling, or daily light exercise.
7. Choose Non-Comedogenic Skincare Products
Non-comedogenic means it won’t clog your pores. Always check product labels — especially for moisturizers, sunscreen, and makeup.
Diet
Many people wonder if their diet affects their skin—and the answer is yes. Research indicates that what you eat can influence the frequency and severity of pimples. While food isn’t the sole cause of breakouts, it plays a significant role.
Below are key diet-related factors supported by credible research.
High-Glycemic Foods
High-GI foods cause quick spikes in blood sugar and insulin, which can lead to excess oil (sebum) and inflammation — two major triggers for pimples. Reducing or avoiding these foods may help keep your skin balanced and clearer.
Foods to Avoid:
- White bread, white rice, and instant noodles
- Cornflakes, puffed rice, and sugary cereals
- Sugary drinks, candies, pastries, and cakes
- Instant mashed potatoes and French fries
- Rice crackers, soda, and processed snacks
- Skimmed dairy (some studies link skim milk to increased breakouts)
Low-Glycemic Foods
Low-GI foods help keep your blood sugar steady, reduce inflammation, and support overall skin healing. They’re packed with nutrients that fight breakouts and support healthy skin cells.
Foods to Eat More Of:
- Omega-3 rich foods: chia seeds, flaxseeds, walnuts, and fatty fish (like salmon, mackerel)
- Legumes: chickpeas, lentils, kidney beans
- Whole grains: barley, quinoa, rolled oats
- Vegetables: spinach, broccoli, cucumber, carrots
- Fruits: apples, oranges, blueberries, and pears
- Full-fat dairy in moderation: plain yogurt, kefir, or milk (if tolerated)
- Nuts & seeds: almonds, pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds
Home Remedies
Some natural remedies may help improve mild pimples in certain people. However, they are not guaranteed to work for everyone, and they are not as effective as proven medical treatments like benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or retinoids. If you have moderate to severe acne, consult a dermatologist for proper care.
1. Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. Studies suggest that a 5% tea tree oil gel may help reduce mild pimples. Always dilute tea tree oil with a carrier oil (like coconut or jojoba oil) before applying to the skin to avoid irritation.
2. Aloe Vera
Aloe vera gel has soothing and healing properties. It may reduce redness and inflammation when applied to pimples. Using pure aloe vera gel is recommended.
3. Honey
Honey, especially raw or Manuka honey, has natural antibacterial effects. Applying a thin layer can calm inflamed pimples and support healing of minor skin lesions.
4. Green Tea (Topical or Oral)
Green tea is rich in antioxidants (EGCG), which may reduce oil production and fight acne-causing bacteria. Applying cooled green tea to the skin or drinking it regularly may help improve skin clarity over time.
5. Zinc (Diet or Supplements)
Zinc is a mineral that supports immune health and oil regulation. Research suggests that zinc supplements or zinc-rich foods such as pumpkin seeds, chickpeas, and nuts may reduce the severity of pimples in some people.
⚠️ Important Note on Home Remedies
Home remedies like tea tree oil, aloe vera, honey, or green tea may help some people reduce pimples, but results can vary. Not every skin type reacts the same way.
what works for one person may cause irritation or no effect for another.If you notice redness, itching, or worsening pimples after trying a remedy, stop using it immediately. For persistent or severe acne, it’s always best to consult a dermatologist for safe and effective treatment options.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)
What causes pimples?
Pimples occur when pores get clogged with oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria. Hormonal changes and excess sebum often trigger acne breakouts.
How can I get rid of pimples fast?
Pimples don’t disappear overnight, but spot treatments with benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid can reduce swelling and redness quickly.
Should I pop a pimple?
No, popping pimples can spread bacteria, worsen acne, and cause scars. It’s better to use a warm compress or medicated cream.
Do certain foods cause pimples?
Some people notice more pimples when eating dairy or high-glycemic foods. While diet affects acne differently for everyone, a balanced diet supports healthy skin.
What’s the difference between acne and pimples?
Pimples are single spots, while acne is the broader skin condition that causes blackheads, whiteheads, and inflamed breakouts.
How long do pimples take to heal?
Most pimples heal naturally within 3–7 days if left untouched, though cystic acne can take longer.
How can I prevent pimples on the face?
Wash your face gently twice a day, avoid oily products, and choose non-comedogenic skincare. Keeping your hands off your face helps reduce pimples.
What home remedies help with pimples?
Natural remedies like diluted tea tree oil, aloe vera gel, or green tea extract may soothe pimples, but results vary.
How can I remove pimple scars?
Pimple marks often fade over time. Using products with retinoids, AHAs, or salicylic acid can speed up fading. Severe acne scars may need professional treatment.
Which products work best for pimples?
Look for cleansers or spot treatments with salicylic acid, benzoyl peroxide, or adapalene. If pimples persist, consult a dermatologist.
Conclusion: How to Prevent Pimples Effectively
Clear skin is achievable with consistent care. Cleanse gently, eat a balanced diet, manage stress, and choose non-comedogenic products. For severe or persistent pimples, consult a dermatologist. Small daily steps lead to long-lasting results.